Published On Jan 31, 2017
A SIMPLE explanation of a Diode. Learn how a Diode works through diagrams and example. Want to know more? Read the full article on the working principle and types of diodes here: https://www.electrical4u.com/diode-wo...
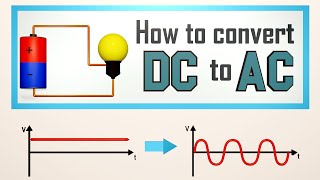
A diode is defined as a two-terminal electronic component that only conducts current in one direction (so long as it is operated within a specified voltage level). An ideal diode will have zero resistance in one direction, and infinite resistance in the reverse direction.
Although in the real world, diodes can not achieve zero or infinite resistance. Instead, a diode will have negligible resistance in one direction (to allow current flow), and very high resistance in the reverse direction (to prevent current flow). A diode is effectively like a valve for an electrical circuit.
Semiconductor diodes are the most common type of diode. These diodes begin conducting electricity only if a certain threshold voltage is present in the forward direction (i.e. the “low resistance” direction). The diode is said to be “forward biased” when conducting current in this direction. When connected within a circuit in the reverse direction (i.e. the “high resistance” direction), the diode is said to be “reverse biased”.
The diode is said to be “forward biased” when conducting current in this direction. When connected within a circuit in the reverse direction (i.e. the “high resistance” direction), the diode is said to be “reverse biased”.
Comment below with any additional questions you have. If you enjoyed this video on diodes and want to see more like it, please LIKE and SUBSCRIBE to our Youtube channel.