Published On Jul 3, 2015
Acute Otitis Media is due to infection or fluid in the middle ear. There must be symptoms and bulging of the tympanic membrane. Which help differentiate it from Otitis Media with Effusion which does not have symptoms or bulging of tympanic membrane. Acute otitis media is very common - up to 90% will have acute otitis media before the age of three.
Anatomy of Middle Ear
The middle ear is located between the tympanic membrane to the internal ear.
What is the pathophysiology of acute otitis media?The eustuchian tube is a canal that goes from ear to the middle ear. When the eustuchian tube becomes edematous the middle ear can no longer drian and there is accumulation of secretions in the middle ear. Common causes for edema of eustuchian tube is upper respiratory tract infection.
Risk factor for acute otitis media include family history, certain age groups, daycare, breast feeding decreases incidence of acute otitis media, pollutants and smoke does have some evidence.
The most common bacterial cause for acute otitis media is strep pneumonia, hemophilus influenza (non-typable), moraxella catarrhalis, Group A strep, staph aureus, Gram negative bacteria. Viruses that cause acute otitis media include respiratory syncytial virus, coronavirus, influenza, adenovirus and metapneumovirus.
CLINICAL SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS of Acute Otitis Media
Fever greater than 104
Otalgia seen as ear rubbing or pulling.
Otorrhea or ear discharge which rules out otitis media with effusion
Otoscopy - Bulging, Decreased mobility, Red (nonspecific)
Tympanogram
Tympanocentesis - identify causative organism
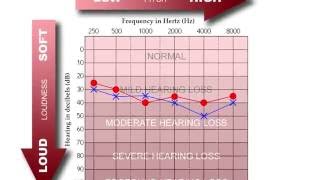
Complications of acute otitis media include haring loss (25 decibels), balance and motor abnormalities, tympanic membrane perforation, cholesteatoma. Infratemporal spread to mastoiditis, petrositis, facial paralysis. Intracranial spread such as meningitis, abscess, epidural and brain, lateral sinus thrombosis, cavernous sinus thrombosis, subdural empyema, carotid artery thrombosis.
TREATMENT
Acute otitis media is the most common conditions for which anti-biotics are prescribed for therefore there is high amount of resistance.
Antibiotics is given if less than 6 months. 6 months to 2 years if severe. Older than 2 years only if otalgia greater than 2 days, fever greater than 102 for 2 days, bilateral, otorrhea.
Observation (2-3 days) 6 months - 2 years non sever (unilateral). If greater than 2 years only if mild symptoms htan give ibuprofen and aceteminophen.
First line anti-biotics for acute otitis media include amoxicillin (90mg/kg/day) and add clavunate if resistant to amoxicillin. If type 1 hypersenstivity give macrolide, or licasonid if type 2 hypersensitivity then give cephalosporin.
If less than 2 years old give for 20 days, if greater than 2 years old give for 5-7 days. Follow up to make sure there are no issues with speech.
Treatment failure is defined as no improvement for 2-3 days. This occurs if the organism is resistant or there is different organism.