Published On Sep 15, 2023
#prokaryoticcells, #eukaryoticcells, #nucleus, #membrane-boundorganelles, #cellsize, #cellshape, #ellwall,c #flagella, #pili, #ribosomes, #DNAreplication, #reproduction
In this video, we will discuss the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are the simplest type of cells, and they are found in bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells, and they are found in all other living organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi.
We will discuss the following differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
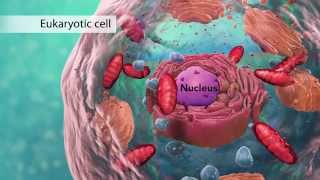
Nucleus: Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. Their DNA is concentrated in a region called the nucleoid, which is not surrounded by a membrane. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that is surrounded by a double membrane. The nucleus contains the cell's DNA, which is organized into chromosomes.
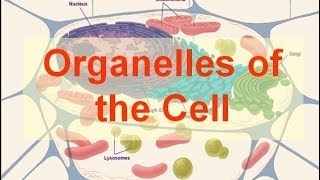
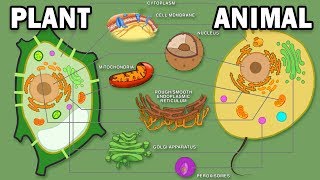
Membrane-bound organelles: Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles. Their DNA, ribosomes, and other cellular components are located in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells have many membrane-bound organelles, including the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. These organelles perform specialized functions that help the cell to survive and function.
Cell size: Prokaryotic cells are generally much smaller than eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells typically range in size from 0.1 to 5 micrometers (μm), while eukaryotic cells typically range in size from 10 to 100 μm.
Cell shape: Prokaryotic cells are typically more irregular in shape than eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells can be spherical, rod-shaped, spiral-shaped, or comma-shaped. Eukaryotic cells are typically more complex in shape and can be round, oval, rectangular, or even star-shaped.
Cell wall: Prokaryotic cells often have a cell wall, while eukaryotic cells generally do not. The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides protection and support for the cell. Prokaryotic cell walls are made of peptidoglycan, while eukaryotic cell walls are made of cellulose or chitin.
Flagella: Prokaryotic cells may have flagella, which are long, whip-like structures that help the cell to move. Eukaryotic cells may also have flagella, but they are typically shorter and more complex than prokaryotic flagella.
Pili: Prokaryotic cells may have pili, which are short, hair-like structures that help the cell to attach to other cells or surfaces. Eukaryotic cells do not have pili.
Ribosomes: Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells both have ribosomes, which are structures that synthesize proteins. However, prokaryotic ribosomes are smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes.
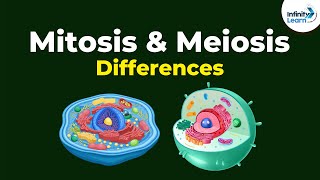
DNA replication: Prokaryotic cells replicate their DNA by a process called binary fission. Eukaryotic cells replicate their DNA by a process called mitosis.
Reproduction: Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually by binary fission. Eukaryotic cells can reproduce asexually by mitosis or sexually by meiosis.
I hope this video has helped you understand the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Thanks for watching!