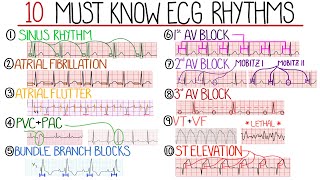
Published On Nov 24, 2023
🩺 ECG Course:
https://www.udemy.com/course/ecgguide
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a type of abnormal heart rhythm, or arrhythmia, that originates above the heart's ventricles. The heart is made up of four chambers: two upper chambers called atria and two lower chambers called ventricles. SVT occurs when there is a malfunction in the heart's electrical system, causing the heart to beat faster than normal.
SVT is characterized by a rapid heart rate that starts and ends suddenly. During an episode of SVT, the heart can beat at a rate of more than 100 to 250 beats per minute, which is much faster than the normal heart rate at rest (60-100 beats per minute). These rapid heartbeats are often felt as palpitations in the chest, throat, or neck.
There are several types of SVT, including:
1. **Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)**: This is the most common type of SVT and occurs due to an abnormal electrical pathway in the heart's atrioventricular node.
2. **Atrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia (AVRT)**: This type of SVT involves an extra electrical pathway between the atria and ventricles, leading to rapid heartbeats.
3. **Atrial Tachycardia**: This occurs when abnormal electrical signals in the atria cause a rapid heartbeat.
4. **Atrial Fibrillation**: Although atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a type of arrhythmia, it can also cause rapid and irregular heartbeats, sometimes falling under the category of SVT.
The exact cause of SVT can vary and may include heart defects present at birth, abnormal electrical pathways in the heart, certain medications, excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption, high levels of stress or anxiety, and other medical conditions.
Diagnosis of SVT usually involves an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) to record the heart's electrical activity during an episode. Holter monitoring and event monitors can also be used to capture intermittent SVT episodes.
Treatment options for SVT depend on the frequency and severity of the episodes. Some mild cases may not require treatment, while more frequent or severe episodes might be managed with medications that regulate the heart's rhythm. In certain cases, a procedure called catheter ablation may be recommended. During this procedure, a catheter is used to destroy the abnormal heart tissue responsible for the rapid heartbeats.
It's important for individuals experiencing symptoms of SVT, such as palpitations, dizziness, chest pain, or shortness of breath, to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and management.
- - - - - - - - - -
Music by INOSSI
Listen: https://bit.ly/3mIA24Z
Watch: • INOSSI - Illusion (Official)
- - - - - - - - - -