Published On Dec 23, 2009
UPDATE: There is an updated version of this animation! Check it out here: • Ovulation
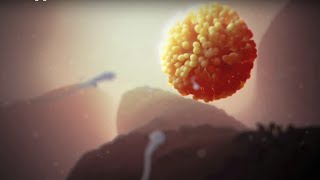
Ovulation is the part of the menstrual cycle where the ovary releases an egg to be fertilized during conception, or sloughed off during a woman's period. This 3D medical animation depicts in exquisite detail: follicle development within the ovary, the movement of the fimbriae over the ovulation site before ovulation, the bursting of the egg from the ovary in a rush of fluid, delicate quality of the ciliated fimbriae and its movement to pick up the egg after ovulation, peristalsis of the fallopian tube to move the egg toward the uterus. Ovulation must take place in order for a woman to get pregnant, preceding the meeting of the male sperm during fertilization.
#Ovulation #MenstrualCycle #Period
ANH09353
Transcript:
Ovulation is a part of the menstrual cycle when the ovary releases a ripe egg, or ovum.
Inside the ovary are hundreds of thousands of follicles. Each follicle is a hollow ball of cells with an immature egg in the center.
The typical 28-day menstrual cycle begins on the first day of menstrual bleeding.
During the first 7 days of the cycle, a few follicles begin to grow at the same time.
These maturing follicles secrete estrogen hormone into the blood stream to prepare the lining of the uterus for pregnancy.
Around Day 7, all of the follicles stop growing and begin to degenerate except for one.
This dominant follicle continues to grow and nourishes the developing egg inside it.
Around Day 12, the follicle secretes a large amount of estrogen into the blood stream.
When the estrogen reaches the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland in the brain, the anterior or front part of the pituitary gland releases a huge surge of luteinizing hormone into the blood stream.
Around day 14, luteinizing hormone causes the follicle to undergo a sudden growth spurt.
Right before ovulation, the egg detaches from the inside of the follicle.
The bulging follicle releases chemicals, causing one of the two fallopian tubes to move in closer and surround the follicle.
The follicle swells until... it bursts open, ejecting the egg and fluid from the follicle into the abdominal cavity.
In response, the fimbriae, tiny projections at the end of the fallopian tube, sweep across the ovulation site and pick up the egg.
Microscopic cilia on the fimbriae's surface transport the egg to the entrance of the fallopian tube.
Inside the walls of the fallopian tube, muscular contractions gently push the egg toward the uterus.
After ovulation, the egg lives for 12-24 hours, so it must be fertilized by a sperm from the male during this time for a woman to become pregnant.
If it is not fertilized, the egg dissolves away and is shed along with the uterine lining during menstruation.