Published On Jul 16, 2017
Protein Synthesis | Cells | Biology | FuseSchool
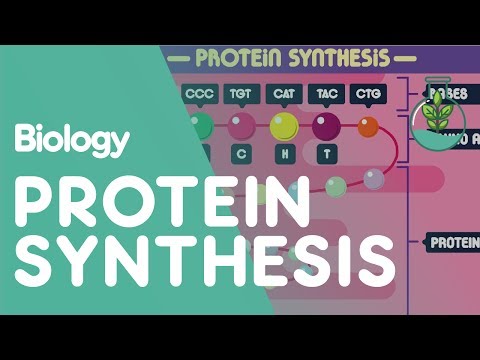
Proteins are made of a long chain of amino acids, which has been coded for by DNA. The order of the bases of DNA determines which protein is made, by coding for a specific order of amino acids. This is protein synthesis, and in this video we are going to look at how it works. You may want to watch our ‘what is DNA’ video first to remind yourself all about DNA.
A set of three bases in the DNA molecule codes for a particular amino acid. GGT, for example, codes for the amino acid called Glycine. The 3 base codes are known as codons, so GGT is a “codon” for Glycine.
There are 20 amino acids that make up our body’s proteins. 9 of these we need to take in through our diet as our body cannot manufacture them. These are known as essential amino acids.
Our body can, however, manufacture non-essential amino acids. Whilst 20 amino acids build proteins, there are actually many others that do not form proteins, possibly over 250. They may form sugar, for example.
Before we start, you need to know what RNA is - so you may want to watch our ‘what is RNA’ video first.
The DNA is in the nucleus and cannot move, but the ribosomes in the cytoplasm are where the proteins are made. This means the code from the DNA needs to be copied and carried across to the ribosome by a molecule called messenger RNA or mRNA before the protein can be made. Let’s have a look at how this all works.
In the nucleus, the enzyme RNA polymerase unwinds and unzips the two strands of DNA that contain the protein-making gene. Only one of these strands is going to be replicated. Complementary RNA nucleotides base pair with the chosen strand. RNA polymerase also binds the RNA nucleotides together making a new RNA strand. This is the messenger RNA or mRNA. This process inside the nucleus is called transcription.
The mRNA travels from the cell nucleus and out into the cytoplasm, until it reaches and attaches to a ribosome. The ribosome then sticks amino acids together to make a polypeptide chain, following the order of amino acids as coded by the mRNA. Three base codons on the mRNA code for one amino acid. This process is called translation.
Let’s look at translation in a little more detail - what is actually happening inside the ribosome...
Transfer RNA or tRNA molecules, carrying specific amino acids, base pair with the mRNA inside the ribosome. So the tRNA brings in the amino acids and the mRNA provides the information of the exact order that the amino acids need to be bonded together in, to ensure the correct protein is made. As more tRNAs match up with the mRNA, the amino acid chain becomes longer. Eventually the polypeptide chain will form into the protein. So there we have protein synthesis.
Inside the nucleus, the DNA molecule is unzipped from around the gene by DNA polymerase. The DNA is replicated and mRNA is formed in the process of transcription. The mRNA travels out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm, where it binds with a ribosome. In the ribosome, the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA is translated by tRNA molecules which carry related amino acids. The polypeptide chain is formed, and will eventually fold into the required protein.
SUPPORT US ON PATREON
/ fuseschool
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
VISIT us at www.fuseschool.org, where all of our videos are carefully organised into topics and specific orders, and to see what else we have on offer. Comment, like and share with other learners. You can both ask and answer questions, and teachers will get back to you.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Find all of our Chemistry videos here: • CHEMISTRY
Find all of our Biology videos here: • BIOLOGY
Find all of our Physics videos here: • PHYSICS
Find all of our Maths videos here: • MATHS
Instagram: / fuseschool
Facebook: / fuseschool
Twitter: / fuseschool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the FuseSchool platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: / fuseschool
Befriend us: / fuseschool
This is an Open Educational Resource. If you would like to use the video, please contact us: [email protected]