Published On Dec 22, 2016
In this video, I'll teach you the difference between the electrical quantities of Impedance (Z), Admittance (Y), Reactance (X), Inductance (L), Capacitance (C), Conductance (G), and Susceptance (B)?
👉 Visit the full article on Impedance (Z), Admittance (Y), Reactance (X), Inductance (L), Capacitance (C), Conductance (G), and Susceptance (B):
http://www.electricalpereview.com/imp...
There are many different types of impedance components and they all rhythm, making it hard to remember which one is which.
Many even have the same units, which can lead to even further confusion.
Don’t let the same “-tance” ending fool you.
If you run into a question on the Electrical PE Exam that asks to solve for one of these components and you aren’t familiar with the exact differences, then you could end up bubbling the wrong answer even if your math and calculations are sound.
Chances are, you’ve already run into a similar mistake or headache while working sample exam practice problems.
To make sure this doesn’t happen on the exam day, let’s take a look at all the different components and define them, as well as understand where each comes from.
(Z) Impedance - A complex number. Opposes the flow of current. Impedance is the sum of resistance and reactance. Z = R+jX [Ω]
(R) Resistance - opposes the flow of current. Real component of impedance R=Re{Z} [Ω].
(X) Reactance - Opposes the change of either current or voltage. Imaginary component of Impedance X=Img{Z} [Ω]
(XL) Inductive Reactance - Reactance that opposes the change of current from an inductance component. XL = 2πfL [Ω]
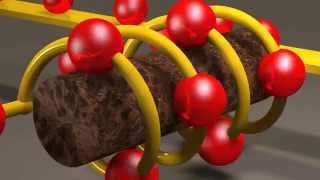
(X) Inductance - A reactive impedance component made out of a coil that creates a strong magnetic field created by current flowing through the shape of a coil. [H]
(XC) Capacitive Reactance - Reactance that opposes the change of voltage from a capacitance component. XC = 1/(2πfC) [Ω]
(C) Capacitance - A reactive impedance component made out of two conducting plates that never physically touch separated by a dielectric medium that creates a polar build up of charge [F]
(Y) Admittance - How easily current can flow, or how well current is admitted. A complex number. The inverse of impedance Y = (1/Z) and the sum of conductance and susceptance Y = G+jB [S]
(G) Conductance - How well a circuit will conduct current. The inverse of resistance and the real component of admittance. G = Re{Y} [S]
(B) Susceptance - How easily a voltage or current can change in a circuit, or how susceptible a circuit is to the change of voltage or current. The inverse of reactance and the imaginary component of admittance. G = Img{Y} [S]
Units:
[Ω] - Ohms
[H] - Hemrys
[F] - Farads
[S] - Siemens or Mhos
__________________________________
👉 Visit the full article on Impedance (Z), Admittance (Y), Reactance (X), Inductance (L), Capacitance (C), Conductance (G), and Susceptance (B):
http://www.electricalpereview.com/imp...
.
**** PE EXAM ***
🔥 SUBSCRIBE for more videos on how to pass the NCEES® Electrical Power PE Exam!
/ @electricalpereview
.
🚀 Ready to PASS the NCEES® Electrical Power PE Exam? Sign up for our FREE online study program for the PE Exam:
https://courses.electricalpereview.co...
.
👀 Electrical Engineering PE Practice Exam and Technical Study Guide by Zach Stone, P.E.:
https://amzn.to/2zKz17u
.
*** FE EXAM ***
⚡ Looking for help with the NCEES® Electrical and Computer FE Exam? Visit our FE Exam Youtube Channel:
/ @electricalfereview7050
.
👇 Ready to pass the NCEES® Electrical and Computer FE Exam? Sign up for our FREE online study program for the FE Exam:
https://www.electricalfereview.com
https://www.electricalfereview.com