Published On May 20, 2023
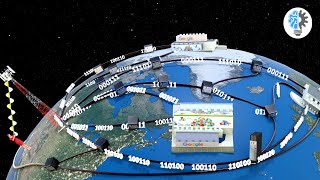
In 1957, the USSR launched Sputnik into orbit. This was the first time a man-made satellite was launched into space. The Cold War caused a race between the world’s 2 superpowers to see who would progress more in space. The launching of Sputnik was a huge win for the Soviets, but what happened next was much better for the U.S. in the long run. When observing the waves coming from Sputnik, scientists at MIT notice something interesting. The frequency of the signals transmitted by it was higher when it was getting closer and lower when it was moving further away. This is the result of the Doppler effect. A phenomenon where the frequency of a wave changes depending on the relative movement between the source and the observer. This means by using 3 or 4 satellites and calculating your distance from them, your exact location on the Earth could be pinpointed. Thus GPS was born. Providing positioning, navigation, and timing services for millions every day, GPS is still relevant to this day. Different countries and continents have a version similar to it in service. Russia has GLONASS and Europe has GALILEO. Even Japan is developing its own GNSS called QZSS, which is expected to be fully operational in 2024. The USSR might have won a small victory with Sputnik, but the birth of GPS was a better outcome than the U.S. could ever think of.
Join our YouTube channel by clicking here: https://bit.ly/3asNo2n
Find us on Instagram: https://bit.ly/3PM21xW
Find us on Facebook: https://bit.ly/3t2Huvb
Find us on Twitter: https://bit.ly/3wQfXzA
Find us on TikTok: https://bit.ly/3wNsBOu
Get the latest stories: https://interestingengineering.com/
Support IE for high-quality journalism: https://interestingengineering.com/su...